Relative to King Arthur’s people, the story unfolds in a captivating setting, where the historical backdrop and cultural tapestry intertwine to create a narrative that is both enchanting and thought-provoking.
From the societal structure and beliefs of the time to the literary representations and archaeological evidence, this topic invites us on a journey through the annals of history and the realm of imagination.
Historical Context
King Arthur, a legendary figure from British folklore, is said to have lived during the 5th or 6th century AD, in the aftermath of the Roman Empire’s withdrawal from Britain. This period, known as the Dark Ages, was a time of great upheaval and uncertainty, as various Germanic tribes and local Celtic populations vied for power in the power vacuum left by the Romans.
Society during this time was largely agrarian, with a hierarchical structure based on land ownership and military prowess. At the top of the social pyramid were the kings and their warlords, who controlled vast estates and commanded armies. Below them were the free peasants, who farmed the land and provided labor for the aristocracy.
At the bottom of the social ladder were the slaves, who had no rights and were often treated as property.
Social Structure
The social structure of Arthur’s time was complex and fluid, with various social classes and groups interacting in different ways. The following is a brief overview of the main social classes:
- Kings and Warlords:The highest-ranking members of society, who controlled vast estates and commanded armies. They were responsible for maintaining order and defending their territories from invaders.
- Free Peasants:The backbone of the economy, who farmed the land and provided labor for the aristocracy. They were generally free men, but they could be forced to serve in the army or pay taxes to the king.
- Slaves:The lowest-ranking members of society, who had no rights and were often treated as property. They were used as laborers, servants, and concubines.
Cultural Customs and Beliefs: Relative To King Arthur’s People

King Arthur’s people adhered to a strict code of honor, chivalry, and loyalty. Chivalry emphasized courtesy, bravery, and protection of the weak. Honor dictated that knights uphold their promises and defend their reputation. Loyalty bound knights to their lords and fellow warriors.
Religious Beliefs
Arthur’s people practiced a blend of Celtic paganism and Christianity. They believed in a pantheon of gods and goddesses, including the Celtic god of war, Lugh, and the Christian God. The fusion of these beliefs created a unique religious landscape that influenced their customs and traditions.
Customs and Traditions
* Feasting and Hospitality:Feasts were central to social life, providing opportunities for storytelling, entertainment, and forging alliances. Guests were welcomed with open arms and treated with utmost hospitality.
Tournaments
Knights competed in tournaments to display their prowess, win glory, and impress ladies. These events showcased their skills in jousting, archery, and swordsmanship.
Hunting
Hunting was a popular pastime for both recreation and sustenance. Knights and nobles often organized hunting expeditions, demonstrating their skills and providing food for their people.
Music and Storytelling
Bards and minstrels played a vital role in society, entertaining with tales of chivalry, love, and adventure. Their songs and stories preserved the cultural heritage and inspired the people.
Literary Representations
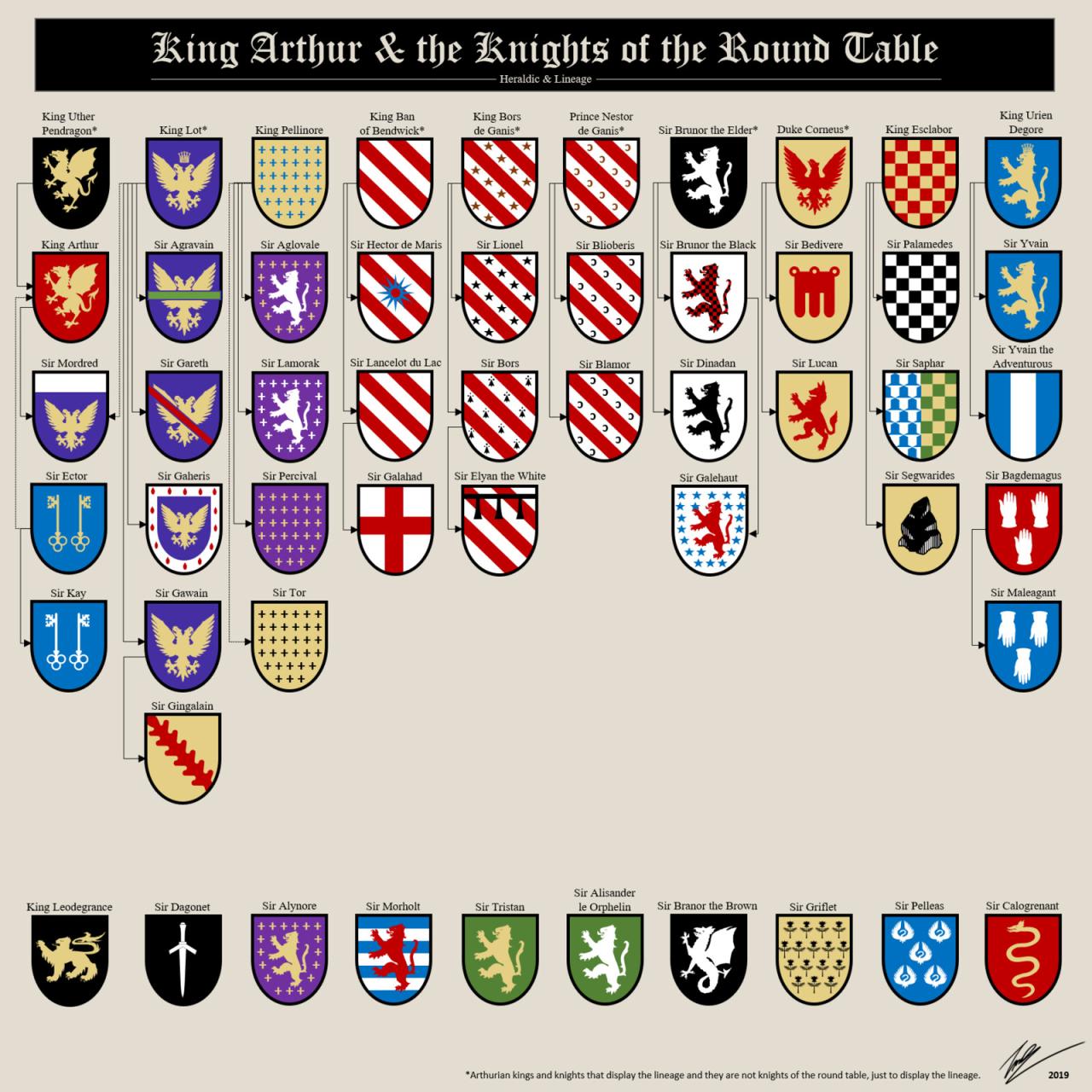
King Arthur and his people have been portrayed in various literary works, most notably in the Arthurian legends and medieval romances. These works have offered diverse interpretations and perspectives on the characters and their world.
Arthurian Legends
The Arthurian legends, a collection of medieval tales and poems, depict King Arthur as a legendary British king who ruled during the 6th century. These legends often emphasize the ideals of chivalry, courtly love, and the quest for the Holy Grail.
Some of the most famous Arthurian legends include:
- Sir Gawain and the Green Knight: A chivalric romance that explores themes of honor, loyalty, and the nature of good and evil.
- Le Morte d’Arthurby Sir Thomas Malory: A compilation of Arthurian tales that provides a comprehensive account of Arthur’s life and reign.
- The Mabinogion: A collection of Welsh mythological tales that include several Arthurian legends.
Medieval Romances
Medieval romances, popular during the Middle Ages, often featured King Arthur and his knights as characters. These romances were typically more fantastical and adventurous than the Arthurian legends, incorporating elements of magic, love, and heroism. Some well-known medieval romances include:
- The Romance of Tristan and Iseult: A tragic love story between a knight and a princess, set in the Arthurian court.
- The Quest of the Holy Grail: A story about the search for the legendary chalice used by Jesus at the Last Supper.
- The Faerie Queeneby Edmund Spenser: An epic poem that allegorically depicts the adventures of King Arthur’s knights.
Archaeological Evidence

While there is no definitive archaeological evidence that conclusively proves the existence of King Arthur and his people, several discoveries have shed light on the historical period in which they are believed to have lived.
One of the most significant archaeological finds is the discovery of a Roman fort at Tintagel Castle in Cornwall, which is traditionally associated with Arthur’s birthplace. Excavations at the site have revealed evidence of a substantial Roman presence in the 5th and 6th centuries, suggesting that the area was a strategic military stronghold during the time when Arthur is believed to have lived.
Limitations and Challenges
Interpreting archaeological evidence in the context of King Arthur’s existence presents several challenges. Firstly, the historical record from this period is fragmentary and often unreliable, making it difficult to establish a clear chronology of events.
Additionally, many of the archaeological sites associated with Arthur have been subject to extensive excavation and reconstruction over the centuries, making it challenging to determine which features are original and which have been added or altered later.
Impact on Society
The legend of King Arthur and his people has left an enduring legacy on Western culture. Their stories have been told and retold for centuries, inspiring countless works of art, literature, and music.
The Arthurian legend has also had a significant impact on our values and traditions. The ideals of chivalry, honor, and courage that are associated with Arthur and his knights have become deeply ingrained in our culture. These ideals continue to inspire people today, both in their personal lives and in their interactions with others.
Literature
The Arthurian legend has been a major source of inspiration for writers throughout history. Some of the most famous works of English literature, including Geoffrey of Monmouth’s History of the Kings of Britainand Thomas Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur, are based on the Arthurian legend. These works have helped to shape our understanding of the Middle Ages and have introduced the characters of Arthur, Lancelot, and Guinevere to generations of readers.
Art
The Arthurian legend has also been a popular subject for artists. Many famous paintings, sculptures, and tapestries depict scenes from the Arthurian stories. These works of art have helped to bring the legend to life and have given us a visual representation of the characters and events that are so familiar to us from literature.
Music, Relative to king arthur’s people
The Arthurian legend has also been a source of inspiration for musicians. Many famous operas, symphonies, and songs have been based on the Arthurian stories. These works of music have helped to popularize the legend and have introduced it to a wider audience.
Quick FAQs
Who was King Arthur?
King Arthur is a legendary figure from British history, renowned for his bravery, leadership, and the establishment of the Knights of the Round Table.
What are the Arthurian Legends?
The Arthurian Legends are a collection of stories and tales centered around King Arthur and his court, which have been passed down through generations.
What is the significance of chivalry in the story?
Chivalry played a central role in the culture of King Arthur’s people, emphasizing values such as courage, honor, and loyalty.