Introducing the Macromolecules of Living Things Answer Key, a comprehensive guide to unraveling the intricate world of biological molecules. This resource delves into the fundamental components of life, providing a thorough understanding of their structure, function, and significance in living organisms.
From the complex carbohydrates that fuel our cells to the proteins that orchestrate biochemical reactions, macromolecules play a pivotal role in sustaining life. This key unlocks the secrets of these essential molecules, empowering readers with a deep appreciation for the building blocks of existence.
Macromolecules of Living Things
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are essential for life. They are found in all living organisms and perform a wide variety of functions. Macromolecules are composed of smaller molecules called monomers, which are linked together by chemical bonds. The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates
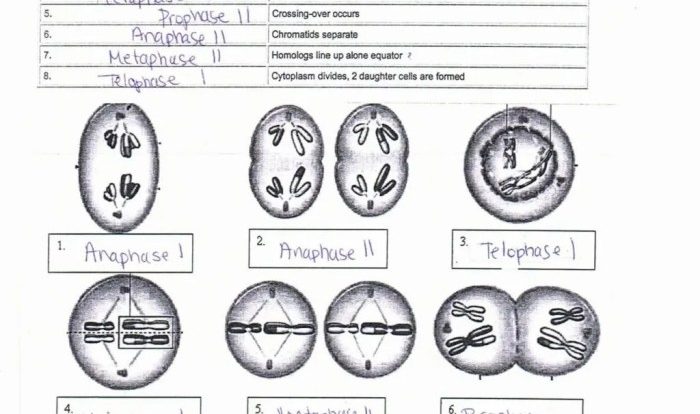
Carbohydrates are a type of macromolecule that provides energy for cells. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and they are classified into three main types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and consist of a single sugar molecule, such as glucose.
Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides linked together, such as sucrose. Polysaccharides are composed of many monosaccharides linked together, such as starch and cellulose.
Types of Carbohydrates
- Monosaccharides: Simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose
- Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides linked together, such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose
- Polysaccharides: Many monosaccharides linked together, such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose
Proteins: Macromolecules Of Living Things Answer Key
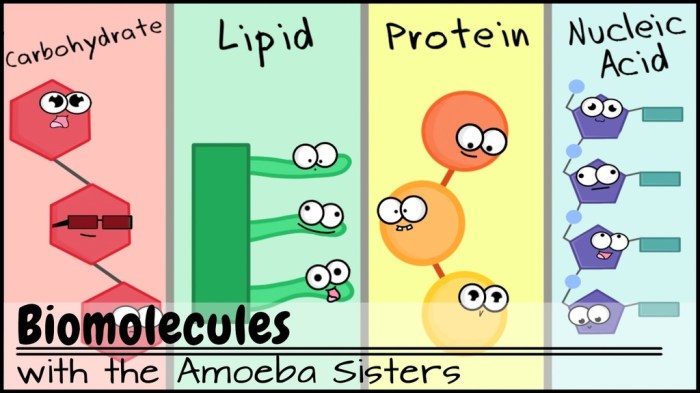
Proteins are a type of macromolecule that is involved in a wide variety of cellular functions, including metabolism, transport, and cell signaling. They are composed of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in various ways to create a wide variety of proteins.
Types of Proteins
- Enzymes: Catalyze chemical reactions in the body
- Structural proteins: Provide support and protection for cells and tissues
- Transport proteins: Move molecules across cell membranes
- Hormones: Regulate body functions
- Antibodies: Protect the body from infection
Lipids
Lipids are a type of macromolecule that is composed of fatty acids and glycerol. They are insoluble in water and are used for energy storage and insulation. There are three main types of lipids: triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Triglycerides are the most common type of lipid and are composed of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule.
Phospholipids are composed of two fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule and a phosphate group. Steroids are composed of four fused carbon rings and are found in hormones and cholesterol.
Types of Lipids
- Triglycerides: Store energy
- Phospholipids: Form cell membranes
- Steroids: Hormones and cholesterol
Nucleic Acids
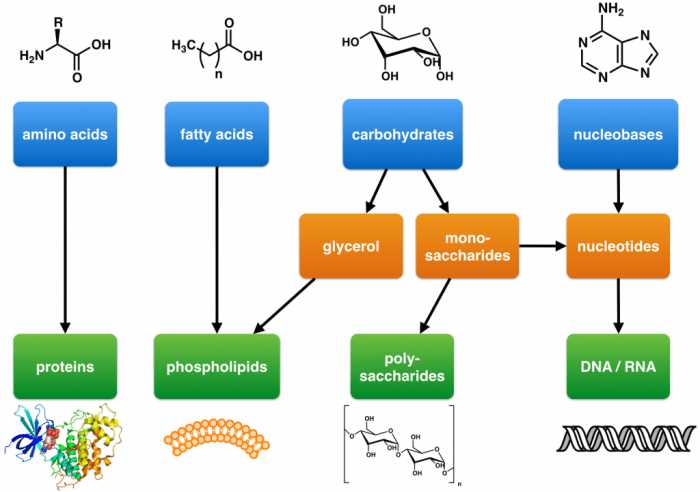
Nucleic acids are a type of macromolecule that is composed of nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. DNA is the genetic material of cells and contains the instructions for making proteins.
RNA is involved in protein synthesis and other cellular processes.
Types of Nucleic Acids, Macromolecules of living things answer key
- DNA: Stores genetic information
- RNA: Involved in protein synthesis
Q&A
What are the four main types of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Energy storage and cellular structure
What are amino acids?
The building blocks of proteins