Reading comprehension is difficult to assess through formal testing alone. – Reading comprehension, a cornerstone of literacy, poses significant challenges when assessed solely through formal testing. This introductory paragraph delves into the intricacies of reading comprehension and the limitations of traditional assessment methods.
Formal testing, while providing standardized measures, often fails to capture the multifaceted nature of reading comprehension. This paper explores alternative methods, cognitive factors, and effective strategies for assessing and enhancing this crucial skill.
1. Introduction

Reading comprehension is a crucial skill in today’s world, enabling individuals to access and comprehend information effectively. However, assessing reading comprehension solely through formal testing presents challenges, as it may not fully capture the complexities of the comprehension process.
2. Methods for Assessing Reading Comprehension
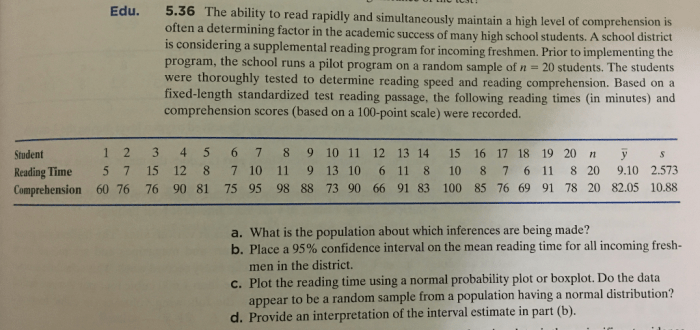
Traditional Testing Methods, Reading comprehension is difficult to assess through formal testing alone.
- Strengths:Objective, standardized, and efficient.
- Weaknesses:May not reflect real-world reading situations, focus on surface-level understanding, and limit insight into students’ thought processes.
Alternative Methods
- Think-aloud protocols:Allow researchers to observe students’ thought processes as they read.
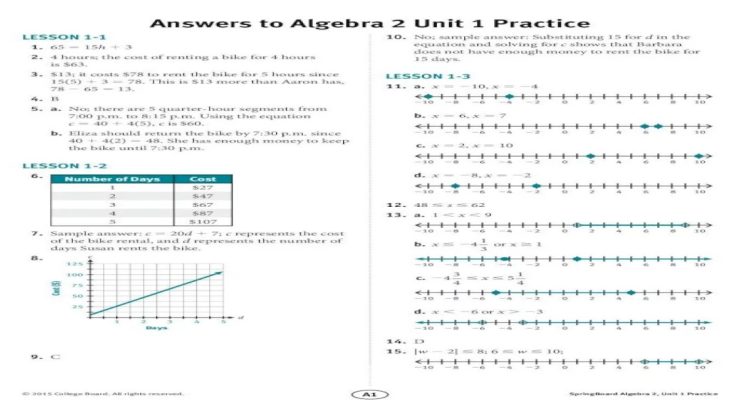
- Retellings:Provide insight into students’ comprehension of the text’s main ideas and supporting details.
- Concept mapping:Help students visualize and organize their understanding of the text.
3. Factors Influencing Reading Comprehension
Cognitive Factors
- Working memory:Holds information temporarily for processing.
- Vocabulary:Knowledge of words and their meanings.
- Background knowledge:Prior knowledge and experiences that support comprehension.
Motivational and Engagement Factors
Motivation, interest, and engagement play significant roles in reading comprehension.
4. Strategies for Improving Reading Comprehension

- Metacognitive strategies:Help students monitor and control their comprehension.
- Text annotation:Encourages active engagement with the text.
- Summarizing:Condenses and clarifies key information.
- Questioning:Promotes critical thinking and deeper understanding.
5. The Importance of Reading Comprehension in Education
Reading comprehension is essential for academic success, enabling students to access and understand a wide range of educational materials.
Poor reading comprehension can hinder students’ overall learning and development, limiting their ability to succeed in various academic disciplines.
Commonly Asked Questions: Reading Comprehension Is Difficult To Assess Through Formal Testing Alone.
Q: Why is reading comprehension difficult to assess through formal testing alone?
A: Formal testing often focuses on discrete skills and provides a limited snapshot of students’ comprehension, failing to capture the dynamic and holistic nature of reading.
Q: What alternative methods can be used to assess reading comprehension?
A: Alternative methods include think-aloud protocols, retellings, concept mapping, and cloze procedures, which provide insights into students’ thought processes and understanding.
Q: What cognitive factors influence reading comprehension?
A: Cognitive factors such as working memory, vocabulary, background knowledge, and metacognitive skills play a significant role in shaping students’ ability to comprehend text.