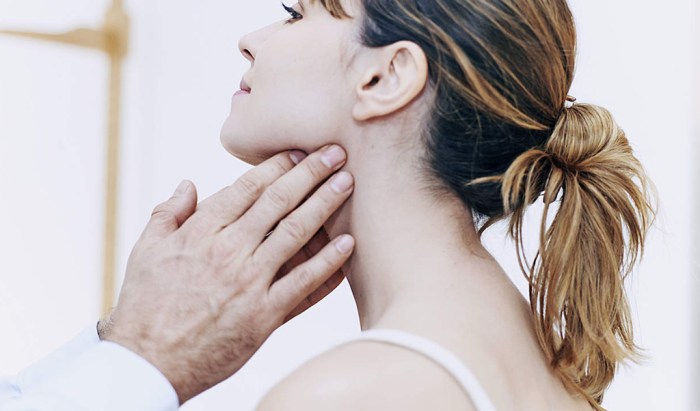
Feeling for swollen lymph nodes is an example of auscultation, a technique used in medical examinations to detect abnormalities. Auscultation involves listening to sounds produced within the body, such as heartbeats, breath sounds, and bowel sounds. By feeling for swollen lymph nodes, healthcare professionals can assess their size, consistency, and tenderness, providing valuable information about underlying medical conditions.
Auscultation is a crucial diagnostic tool in various medical settings. It is used to evaluate heart function, respiratory health, and gastrointestinal function. By listening to specific sounds, healthcare professionals can identify abnormalities such as murmurs, wheezes, and bruits, which may indicate underlying diseases or conditions.
Auscultation Definition and Methods: Feeling For Swollen Lymph Nodes Is An Example Of Auscultation
Auscultation is a medical technique that involves listening to sounds produced within the body, primarily using a stethoscope. It is a non-invasive method that provides valuable information about the functioning of various organs and systems.
There are two main methods of auscultation: direct and indirect. Direct auscultation involves placing the stethoscope directly on the skin, while indirect auscultation uses a diaphragm or bell to amplify the sounds.
Auscultation is used in a wide range of medical settings, including cardiology, pulmonology, and gastroenterology. It can help diagnose conditions such as heart murmurs, lung infections, and abdominal disorders.
Feeling for Swollen Lymph Nodes as a Form of Auscultation
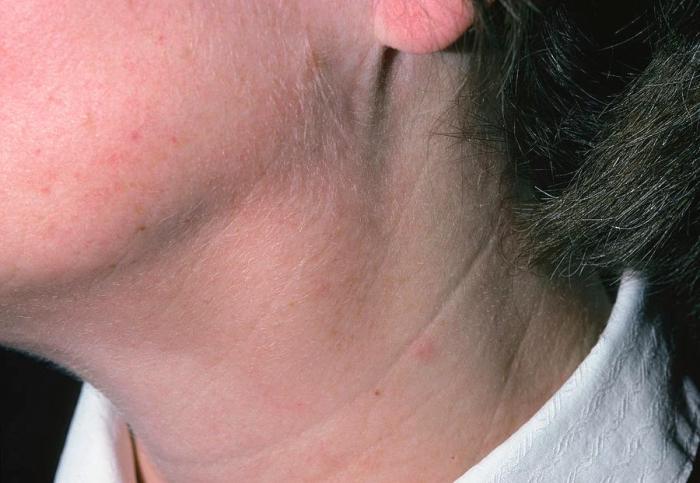
Palpation, which involves feeling with the hands, can also be used as a form of auscultation to detect swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures located throughout the body that play a role in the immune system.
Swollen lymph nodes can indicate an underlying medical condition, such as infection, inflammation, or malignancy. Palpating for swollen lymph nodes can help identify their location, size, and tenderness, which can provide clues to the underlying cause.
To properly palpate for swollen lymph nodes, gently press your fingers around the neck, armpits, groin, and other areas where lymph nodes are commonly found. If you feel any enlarged or tender nodes, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Differential Diagnosis of Swollen Lymph Nodes, Feeling for swollen lymph nodes is an example of auscultation
The differential diagnosis of swollen lymph nodes includes a wide range of possible causes, including:
- Infections (e.g., bacterial, viral, fungal)
- Inflammation (e.g., autoimmune disorders, allergic reactions)
- Malignancies (e.g., lymphoma, leukemia)
Distinguishing between benign and malignant causes of swollen lymph nodes is crucial. Benign causes are typically characterized by gradual onset, smaller size, and lack of tenderness or fixation to surrounding tissues. Malignant causes, on the other hand, may present with rapid onset, larger size, tenderness, and fixation.
The following table summarizes the key characteristics and diagnostic criteria for different causes of swollen lymph nodes:
| Cause | Characteristics | Diagnostic Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Gradual onset, smaller size, tender | History of infection, positive culture or serology |
| Inflammation | Gradual onset, smaller size, non-tender | History of autoimmune disorder or allergic reaction |
| Malignancy | Rapid onset, larger size, tender, fixed | Biopsy |
Clinical Significance and Management of Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes can have significant clinical implications. They may indicate an underlying infection, inflammation, or malignancy. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation to determine the cause and appropriate management.
The management of swollen lymph nodes depends on the underlying cause. Conservative measures, such as antibiotics for infections or anti-inflammatory medications for inflammation, may be sufficient in some cases. In other cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, particularly for malignant causes.
It is important to refer patients with swollen lymph nodes for further evaluation if they have:
- Persistent or enlarging nodes
- Tender or painful nodes
- Nodes that are fixed to surrounding tissues
- Other concerning symptoms, such as fever, weight loss, or night sweats
Expert Answers
What is the purpose of feeling for swollen lymph nodes?
Feeling for swollen lymph nodes helps healthcare professionals assess their size, consistency, and tenderness, providing information about underlying medical conditions.
How can swollen lymph nodes indicate underlying medical conditions?
Swollen lymph nodes can be a sign of infection, inflammation, or malignancy, and their characteristics can help differentiate between benign and malignant causes.
What are the different methods used in auscultation?
Auscultation methods include direct auscultation, using a stethoscope placed directly on the body, and indirect auscultation, using a stethoscope connected to a bell or diaphragm.