Unit 6 outcome 1 meiosis coloring worksheet answer key – Embark on a scientific expedition with our comprehensive guide to the Unit 6 Outcome 1: Meiosis Coloring Worksheet Answer Key. Delve into the intricacies of meiosis, unlocking the mysteries of genetic inheritance and variation.
Through engaging explanations and detailed illustrations, this resource empowers students to grasp the fundamental concepts of meiosis, laying a solid foundation for further exploration in genetics and beyond.
Meiosis Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
A meiosis coloring worksheet is an educational tool designed to facilitate the understanding of the process of meiosis, a type of cell division that produces gametes (sex cells). By coloring different structures involved in meiosis, students can visualize and comprehend the complex stages and events that occur during this crucial process.
Comprehensive Answer Key:
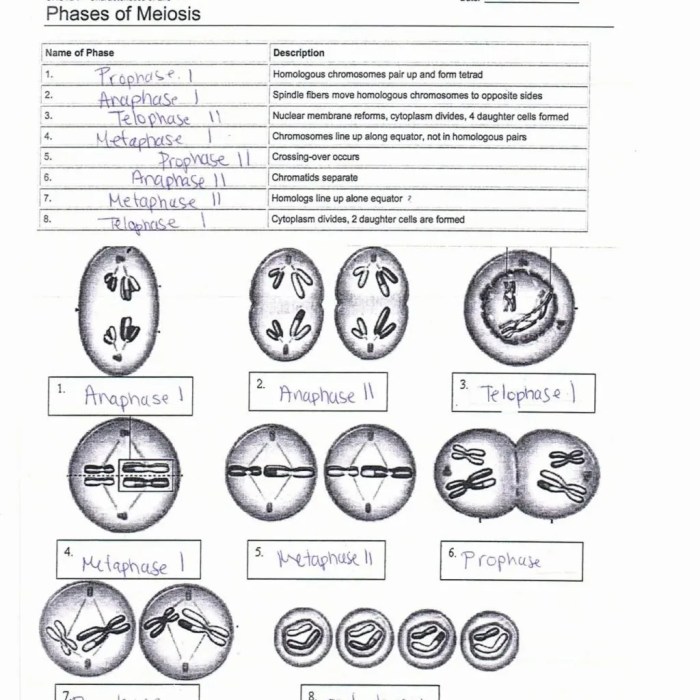
- Prophase I:Homologous chromosomes pair up, forming tetrads. Synapsis and crossing over occur.
- Metaphase I:Tetrads align along the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I:Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I:Cytokinesis occurs, dividing the cell into two haploid daughter cells.
- Prophase II:Chromosomes condense again, and the spindle apparatus forms.
- Metaphase II:Chromosomes align along the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase II:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II:Cytokinesis occurs, dividing each daughter cell into two haploid cells, resulting in a total of four haploid gametes.
Meiosis Process and Stages
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing haploid gametes. It occurs in two sequential divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, each consisting of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase stages.
Prophase I
- Synapsis: Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over.
- Condensation: Chromosomes become visible.
Metaphase I
- Alignment: Tetrads align along the equator of the cell.
- Spindle fibers: Attach to the chromosomes and prepare for separation.
Anaphase I
- Separation: Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase I, Unit 6 outcome 1 meiosis coloring worksheet answer key
- Cytokinesis: The cell divides into two haploid daughter cells.
- Interkinesis: A brief resting phase before meiosis II.
Prophase II
- Condensation: Chromosomes condense again.
- Spindle formation: Spindle fibers form.
Metaphase II
- Alignment: Chromosomes align along the equator of the cell.
Anaphase II
- Separation: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II
- Cytokinesis: The cell divides into two haploid daughter cells.
Homologous Chromosomes and Genetic Variation
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that carry the same genetic information but may have different alleles. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over. This process introduces genetic variation into the gametes, which increases the diversity of offspring.
Crossing Over:
- Segments of homologous chromosomes break and exchange.
- Results in new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes.
Independent Assortment:
- Homologous chromosomes and their alleles are randomly distributed to the gametes.
- Further increases genetic variation in the offspring.
Meiosis in Sexual Reproduction
Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction as it produces haploid gametes that combine during fertilization to form a diploid zygote. This process ensures the maintenance of chromosome number from one generation to the next.
Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|
| One cell division | Two cell divisions |
| Produces two identical daughter cells | Produces four haploid daughter cells |
| No genetic variation | Introduces genetic variation |
Examples of Organisms that Undergo Meiosis
- Humans
- Animals
- Plants
- Fungi
Applications of Meiosis Coloring Worksheets: Unit 6 Outcome 1 Meiosis Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
Meiosis coloring worksheets are valuable tools in education and research:
Education:
- Enhance understanding of meiosis stages and structures.
- Visualize the complex processes involved in meiosis.
- Reinforce learning through hands-on activities.
Research:
- Study genetic variations and inheritance patterns.
- Investigate the role of meiosis in evolution.
Lesson Plan Incorporation:
- Introduce the concept of meiosis.
- Review the stages and structures of meiosis.
- Assess student understanding through coloring exercises.
- Facilitate group discussions and presentations.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of meiosis in sexual reproduction?
Meiosis plays a crucial role in sexual reproduction by ensuring genetic diversity among offspring. It shuffles and recombines genetic material, creating unique combinations of alleles that contribute to the vast array of traits observed in populations.
How does crossing over contribute to genetic variation?
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This exchange results in the formation of new chromosomes that carry a blend of alleles from both parents, increasing genetic diversity.
What are the key differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells. Meiosis involves two rounds of division (meiosis I and meiosis II), whereas mitosis only involves one round of division. Additionally, meiosis includes the process of crossing over, which does not occur in mitosis.
