Match the types of synovial joints in column a – Embark on a journey into the realm of synovial joints, exploring their intricate classification, diverse functions, and clinical significance. This comprehensive guide unveils the fascinating world of joints that facilitate movement and connect bones, providing a deeper understanding of their structure, function, and impact on human health.
Synovial joints, characterized by their fluid-filled cavities and flexible connective tissues, exhibit remarkable diversity in their form and function. Delve into the nuances of synovial joint classification, unraveling the distinct characteristics that define each type. Discover the intricate interplay between joint structure and function, as we examine how the unique architecture of each joint governs its range of motion and adaptability.
Types of Synovial Joints
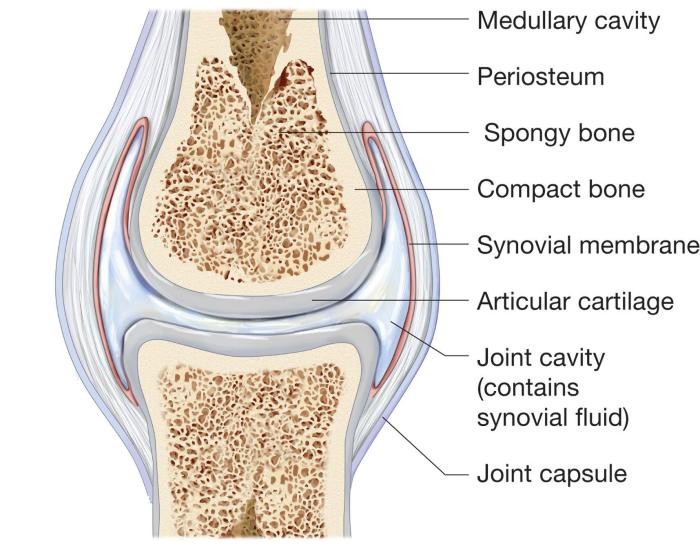
Synovial joints are a type of freely movable joint that allows for a wide range of motion. They are characterized by the presence of a synovial membrane, which lines the joint cavity and secretes synovial fluid. Synovial fluid provides lubrication and nourishment to the joint.
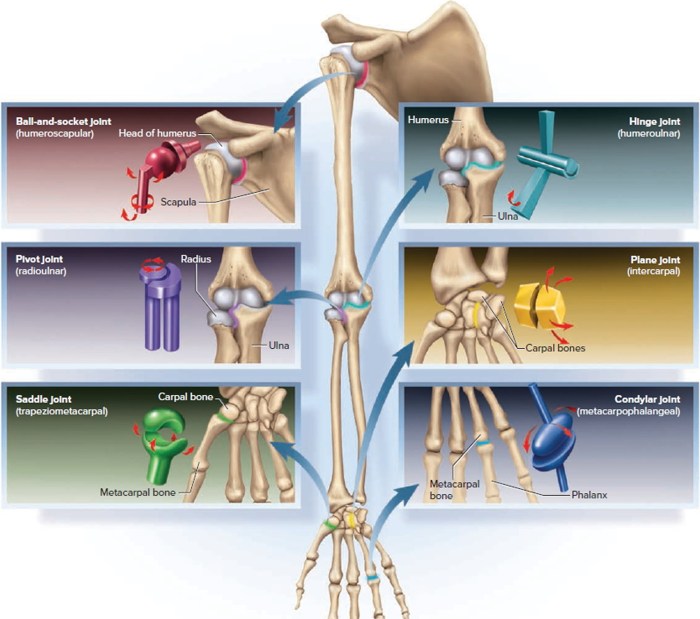
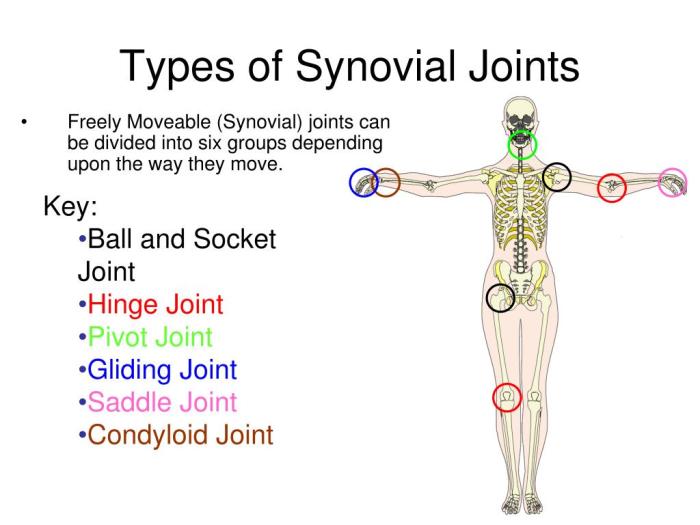
Synovial joints can be classified into six different types based on their shape and range of motion: plane joints, hinge joints, pivot joints, condyloid joints, saddle joints, and ball-and-socket joints.
Plane Joints
- Allow gliding movements in one plane
- Examples: joints between the vertebrae, joints between the carpals in the wrist
Hinge Joints, Match the types of synovial joints in column a
- Allow flexion and extension in one plane
- Examples: knee joint, elbow joint
Pivot Joints
- Allow rotation around a single axis
- Examples: joint between the atlas and axis vertebrae, joint between the radius and ulna
Condyloid Joints
- Allow flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
- Examples: joint between the radius and carpal bones, joint between the metacarpals and phalanges
Saddle Joints
- Allow flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction
- Examples: joint between the thumb and trapezium bone
Ball-and-Socket Joints
- Allow flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction
- Examples: shoulder joint, hip joint
Clarifying Questions: Match The Types Of Synovial Joints In Column A
What are the main types of synovial joints?
Synovial joints are classified into six main types: plane, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket joints.
How does the structure of a synovial joint determine its function?
The shape and orientation of the joint surfaces, as well as the presence of ligaments and other supporting structures, dictate the range and type of motion permitted by a synovial joint.
What are some common injuries associated with synovial joints?
Common injuries include sprains, strains, dislocations, and fractures, which can affect the ligaments, tendons, bones, or joint capsule.