Given a piece of work to be executed in agile, we embark on an exploration of the principles, benefits, and challenges of adopting agile methodologies. This comprehensive guide unveils the transformative power of agile in delivering projects with enhanced efficiency, adaptability, and quality.
Agile methodologies have revolutionized the way we approach work, fostering a collaborative and iterative environment that empowers teams to navigate uncertainty and deliver exceptional results. By embracing agile principles, organizations can unlock a wealth of advantages, including reduced time-to-market, increased customer satisfaction, and improved team morale.
Key Agile Principles: Given A Piece Of Work To Be Executed In Agile
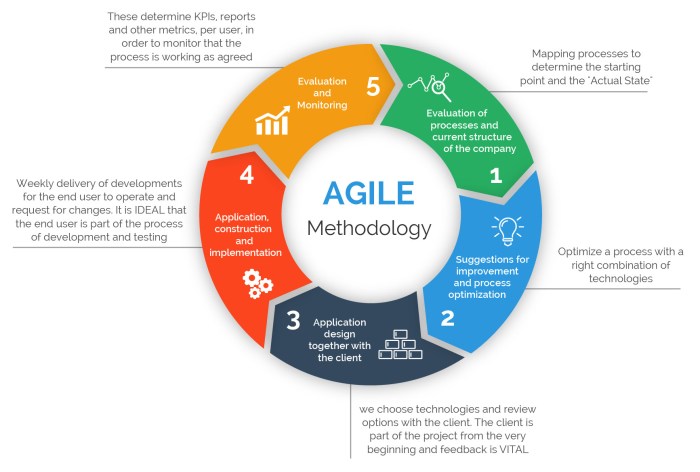
Agile methodologies are founded on a set of core principles that guide the execution of a given piece of work. These principles emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development.
Customer involvement:Agile teams involve customers throughout the development process, gathering feedback and incorporating it into the work. This ensures that the final product meets the customer’s needs and expectations.
Iterative development:Agile teams work in short cycles, or iterations, releasing small increments of the product or service on a regular basis. This allows for continuous feedback and adaptation to changing requirements.
Flexibility:Agile teams are adaptable and responsive to changing priorities and unforeseen circumstances. They embrace change and view it as an opportunity for improvement.
Continuous improvement:Agile teams are committed to ongoing improvement and learning. They regularly reflect on their processes and identify areas for optimization.
Benefits of Agile Execution
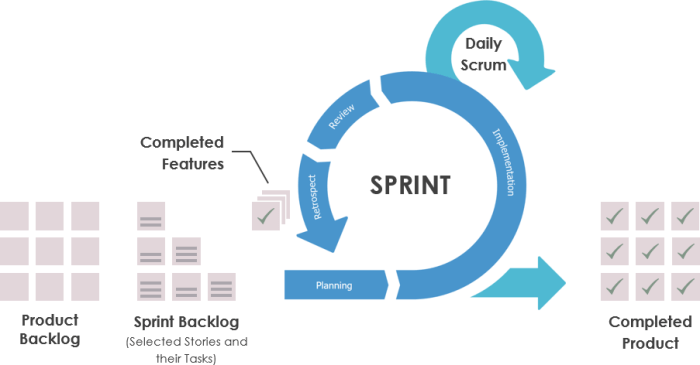
Agile execution offers numerous advantages for executing a given piece of work, including:
- Reduced time to market:Agile methodologies enable teams to deliver working software or services more quickly by breaking down large projects into smaller, manageable tasks.
- Increased flexibility:Agile teams can adapt to changing requirements and market conditions more easily, reducing the risk of costly rework and delays.
- Improved quality:Agile teams focus on continuous testing and feedback, which helps to identify and fix defects early in the development process, resulting in a higher-quality final product.
- Increased customer satisfaction:Agile teams involve customers throughout the development process, ensuring that the final product meets their needs and expectations.
Challenges of Agile Execution
While agile execution offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges, including:
- Managing complexity:Agile methodologies can become complex to manage in large-scale projects or when multiple teams are involved.
- Lack of documentation:Agile teams often prioritize working software over documentation, which can lead to challenges in maintaining a clear understanding of the project.
- Resistance to change:Agile methodologies require a cultural shift within the organization, and some individuals may resist the change from traditional project management approaches.
- Lack of planning:Agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and adaptability, which can lead to a lack of long-term planning and coordination.
FAQ Corner
What are the core principles of agile methodologies?
Agile methodologies are founded on principles such as iterative development, continuous improvement, customer collaboration, and empowering self-organizing teams.
How can agile methodologies benefit organizations?
Agile methodologies offer numerous benefits, including reduced time-to-market, improved product quality, increased customer satisfaction, and enhanced team collaboration.
What are some common challenges in agile execution?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of stakeholder buy-in, and difficulties in scaling agile practices to larger organizations.